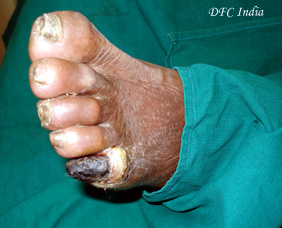
Gangrene is described as dead or dying body tissue due to complete loss of blood supply to the part or inadequate blood supply to keep the tissue viable.
CAUSE OF GANGRENE:
Cells in the body require nutrients and oxygen to survive and they get this from our blood. If their blood supply goes down below a certain level, the cells will become damaged and will eventually die.
Tissues and cells are also attacked by organisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi. If the blood supply is cut there will be no white cells or T-cells to stop t he organisms from multiplying and causing an infection.
RISK FACTORS FOR GANGRENE:
1) Diabetes :
Diabetes affects nerves and when the nerves are damaged, patient does not feel pain and will not when they get injury. The patient may continue walking without protecting the wound. The wound may get worse and develop into a foot ulcer. High blood sugar levels may also damage blood vessels, resulting in poor blood supply to the area. Less blood means less nutrients and oxygen for the tissue cells, and fewer white blood cells and T-cells to fight off infection. The ulcer becomes infected; the infection grows rapidly and gangrene develops.
2) Vascular diseases:
Diseases of the blood vessels such as atherosclerosis (narrowed arteries) and blood clots may block vessel leading to poor or no blood supply to the part.
3) Injury:
Any injury or infection if not treated in time can give rise to gangrene.
4) Smoking :
smoking causes the blood vessels to narrow, resulting in less blood flow.
What are the symptoms of gangrene?
Symptoms of dry gangrene
Generally, dry gangrene develops slowly. It is the most common gangrene for patients with atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases.
It normally does not spread.
A red line appears on the skin, by which the wound is demarcated well.
The area will gradually become numb and cold.
When necrosis (tissue death) occurs there may be some pain.
Some patients, especially older ones, may not feel anything.
The area will change from red, to brown, to black.
The necrotized tissue then shrivels up and eventually falls off.
Symptoms of wet gangrene
Wet gangrene is much more painful than dry gangrene. The term ‘wet’ is used to refer to a bacterial infection in the affected tissue. It can develop as a result of an injury, a severe burn, or frostbite. This type of gangrene is common with diabetes patients who unwittingly injure a toe or foot. As it spreads rapidly and can be fatal it needs to be treated urgently.
The affected area swells before any tissue dies.
The skin will change color from red, to brown, to black.
There will be pus and a foul smell.
Fever (temperature).
Gas gangrene
Usually deep muscle tissue is affected. The surface of the skin may appear normal, but as the condition advances the skin may become pale, and then turn grey or purplish-red. The bacterial infection produces toxins that release a gas. Gas gangrene can become life-threatening.
Fournier’s gangrene:
This type is very uncommon . It affects the male genital organs. It is usually the result of a urinary tract infection or an infection in the genital area. The patient will feel pain, tenderness, and swelling in the affected area.
What is the treatment for gangrene?
Necrotized (dead) tissue cannot be saved, but a lot can be done to stop the gangrene from spreading.
Surgery (Debridement)
The surgical removal of dead tissue (debridement) or amputation of the affected toe or limb helps prevent the gangrene from spreading, and allows healthy tissue to recover.